Unleashing the Power of USB-C: Connecting Your Laptop to a 4K DisplayPort
Table of Contents:
- Introduction
- FPS and Hz
- DisplayPort or HDMI?
- Choosing Between a DisplayPort Cable or Adapter
- USB-C to DisplayPort Capabilities and Compatibility
- Troubleshooting Your Connection
- Conclusion
Introduction
The world of technology is continually evolving, and one of the most significant advancements in recent years is the introduction of the USB-C port. This versatile connector has gradually replaced the traditional USB A and USB B ports on modern laptops, tablets, and smartphones. The USB-C port is not only symmetrical, allowing for easy insertion, but it also unlocks a multitude of capabilities, including high-speed data transfer and power delivery. In this article, we will guide you on how to connect your laptop's USB-C port to a 4K DisplayPort and discuss the benefits of this powerful connection.
USB-C and Cutting-Edge Technologies
The USB-C technology has become synonymous with several groundbreaking features, such as USB 3.1 data transfer (up to 10 Gbps), USB power delivery for laptops, and Thunderbolt 3 compatibility for supported devices. These capabilities enable the USB-C port to output high-quality video content from various devices to high-resolution displays like 4K TVs.
Essential Equipment for a Seamless Connection
To utilize your laptop's USB-C port for 4K DisplayPort video output, you must have the proper cables and adapters to maintain optimal video quality. The necessary components include:
- Laptop with USB-C port
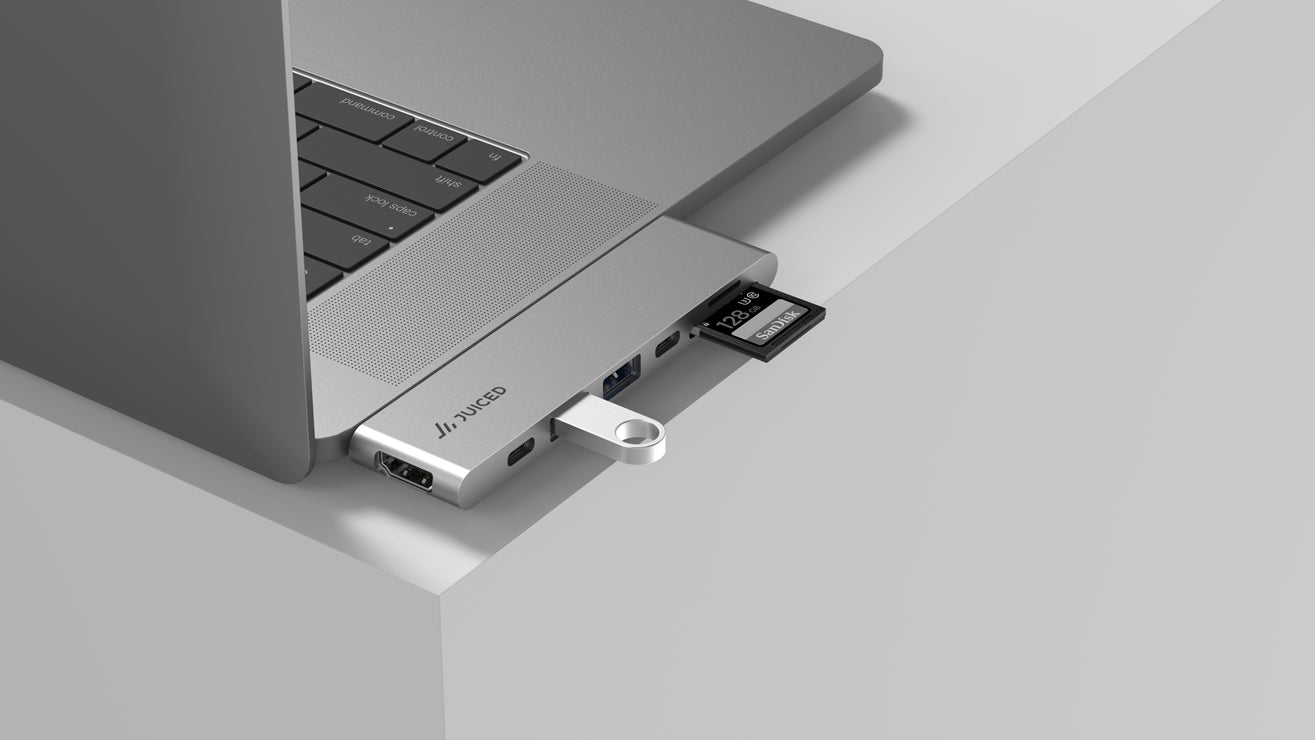
- USB-C to DisplayPort adapter or USB-C to DisplayPort Adapter Cable
- 4K monitor that supports USB-C port
For the best viewing experience, ensure that your laptop, output adapters/cables, and monitor all support the same level of video output/input.
Setting Up Your 4K Connection
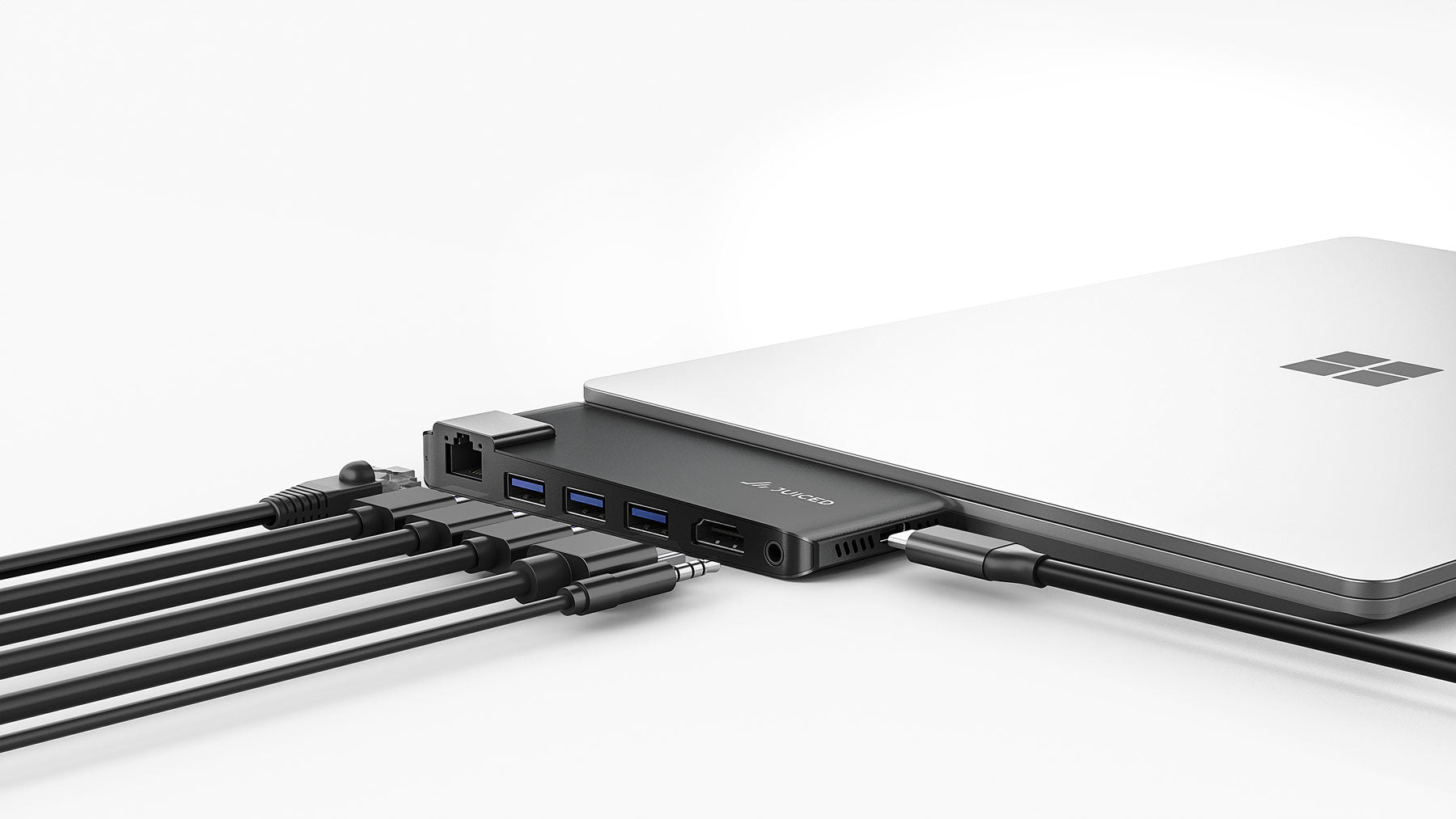
Once you have your device, a laptop USB-C to DisplayPort 4K adapter, and an external display, simply connect the adapter cable from the USB-C port to the DisplayPort. If your TV has an HDMI port instead of a DisplayPort, you will need an additional cable to establish the connection. The USB-C to DisplayPort adapter connects to a hub or another DisplayPort to HDMI cable, which then connects to the HDMI port on the monitor/display.
Understanding FPS and Refresh Rates
It is crucial to consider the video output quality on your laptop in relation to your 4K monitor/display's refresh rate. For instance, if your laptop supports 60 FPS (frames per second), but your 4K display has a 30Hz refresh rate, you will only see 30 frames. This discrepancy can result in screen tearing, where the display combines two frames into one, causing distortion and affecting your viewing experience.
DisplayPorts, even older generations, can support 4K@60Hz viewing, ensuring no loss in video output quality. However, with HDMI, an HDMI 1.4 port can only support 4K@30Hz. To achieve a better viewing experience using HDMI, invest in a high-speed HDMI cable, such as HDMI 2.0, which supports a 60 Hz refresh rate. Keep in mind that maximum resolutions and FPS may also be limited by your operating system or video graphics card. Verify your computer's compatibility with specific video/screen resolutions.
DisplayPort or HDMI: Which Connection to Choose?
When deciding between DisplayPort or HDMI for your laptop USB-C to 4K DisplayPort video output, it is essential to weigh the pros and cons of each. While HDMI is a more common port found on most TVs, DisplayPort offers superior visual quality and performance. DisplayPort versions 1.2 and higher can send 4K video signals up to 3840 x 2160 resolution at 60 Hz, while HDMI ports are limited to 30 Hz for 4K signals. Furthermore, DisplayPort provides the highest bandwidth available for data transmission between your laptop and TV, resulting in better performance and picture quality compared to HDMI connections.
Choosing Between a DisplayPort Cable or Adapter
When connecting a device with a USB-C port to a display with a DisplayPort connection, you will need either a cable or an adapter. The choice depends on the type of connection required and the device you are using.
A cable is the simplest option if your device doesn't support video output over USB-C. Direct cable connections are fast, easy, and reliable - simply plug in the cable, and you're good to go. However, these cables can be expensive and may not be cost-effective for infrequent use. Additionally, video output quality may be reduced due to bandwidth limitations, especially if your source device doesn't support Display Stream Compression (DSC). Some cables also require external power, adding extra cost and complexity.
On the other hand, adapters offer more flexibility when connecting USB-C devices to DisplayPort displays. They are available in various sizes and shapes and are generally more affordable than cables. Adapters can support higher resolutions and color spaces, such as 8K@60Hz UHD.
USB-C to DisplayPort connections enable users to link their USB-C-enabled devices, like laptops or smartphones, to monitors or other displays with a DisplayPort interface. This connection facilitates the transfer of audio, video, and data signals between the two devices.
DisplayPort, developed by the Video Electronics Standard Association (VESA), is primarily used to connect a video source to a display device, such as a computer monitor. It can also carry audio, USB, and other data types. The latest version of DisplayPort (version 1.4) supports resolutions up to 8K UHD (7680×4320) at 60Hz with 10-bit color depth.
USB-C or Thunderbolt 3 port is a USB connection type developed by the USB Implementers Forum (USB-IF). It offers higher data transfer speeds and power delivery than previous USB generations. Thunderbolt 3 ports can handle data transfer speeds up to 40Gbps and deliver up to 100W of power.
For a successful connection between the two devices, both must support DisplayPort Alternate Mode (DP Alt Mode). This mode allows for conversion between DisplayPort signals and USB-C signals without additional adapters or cables. Some devices may require extra adapters to work properly; consult your device's manual for specific connection instructions.
Here is a brief explanation of DP Alt Mode.
DisplayPort Alternate Mode (DP Alt Mode) is a specification that allows some USB-C ports to output a DisplayPort signal. This allows USB-C devices, such as laptops and tablets, to be connected directly to monitors or TVs using a single cable. It utilizes the existing DisplayPort technology for video and audio transmission, but transmits it through the USB-C connection. In addition, a device that supports DP Alt Mode can also provide power to the connected display.
In order to use DisplayPort Alternate Mode, both devices must support it and have compatible cables or adapters. Cable Matters USB-C to DisplayPort 1.4 cable is an example of a high-quality cable that supports 8K@60Hz video resolutions and is also backward compatible with lower resolutions such as 1080p.
Troubleshooting Your Connection
If you encounter issues when turning on your display or monitor, check the following:
- Ensure the laptop USB-C to DisplayPort 4K connection is secure on both the laptop and display sides.
- Verify that the video cable is securely plugged into the monitor/display and the adapter.
- Disconnect and reconnect the adapter on your laptop side and observe any changes. If there is no change, disconnect and reconnect the video cable from the adapter.
If these steps do not resolve the issue, your cable(s) may be malfunctioning, and you may need to replace them. Test the cable using a different USB-C device, such as your smartphone or tablet.
Conclusion
Connecting a laptop with a USB-C port to a 4K DisplayPort requires attention to frame rates and refresh rates to prevent limiting video output. DisplayPort is inherently compatible with 4K resolution at 60 Hz, while HDMI may require additional considerations. By understanding the capabilities and limitations of USB-C and DisplayPort connections, you can optimize your viewing experience and harness the full potential of your devices.
Comparison Table: Display to USB-C Cables, DisplayPort to HDMI Cables, DisplayPort to Adapter
| Type | Video Resolution | Audio Support | Bi-Directional | Connector Types | Typical Use Cases |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Display to USB-C Cables | Up to 4K@60Hz | Yes | No | DisplayPort/Mini DisplayPort to USB-C | Connecting USB-C devices to DisplayPort enabled monitors or TVs |
| DisplayPort to HDMI Cables | Up to 4K@60Hz | Yes | No | DisplayPort/Mini DisplayPort to HDMI | Connecting DisplayPort enabled devices to HDMI monitors, TVs or projectors |
| DisplayPort to Adapter | Depends on adapter | Depends on adapter | Depends on adapter | DisplayPort/Mini DisplayPort to various output types (e.g., HDMI, DVI, VGA, USB-C) | Connecting DisplayPort enabled devices to various display types |