Unleashing the Power of 2.5 Gbps Ethernet: The New Networking Standard Transforming Connectivity and Performance
Introduction to 2.5 Gbps Ethernet
In today's digital landscape, 2.5 Gbps Ethernet has emerged as the new gold standard, superseding the once-dominant 1 Gbps Ethernet. This cutting-edge technology provides faster, more reliable, and efficient data transfer capabilities, making it an essential component of modern networking infrastructures.
The Evolution of Ethernet Standards
As the backbone of countless networks worldwide, Ethernet technology has undergone numerous advancements since its inception in the 1970s. Over the years, the industry has seen several Ethernet standards, each with improved speeds and capabilities:
- 10 Mbps (10BASE-T): Introduced in the early 1990s, this standard was the first widely adopted Ethernet technology.
- 100 Mbps (100BASE-TX): Commonly known as Fast Ethernet, this version emerged in the mid-1990s and provided a tenfold speed increase.
- 1 Gbps (1000BASE-T): Gigabit Ethernet, introduced in the late 1990s, marked a significant leap in data transfer speeds.
- 10 Gbps (10GBASE-T): This standard, introduced in the mid-2000s, offered a tenfold increase in performance over its predecessor.
The 2.5 Gbps Ethernet standard is the latest development in this evolutionary process, filling the gap between 1 Gbps and 10 Gbps technologies. It provides a cost-effective and energy-efficient solution for organizations seeking to enhance their network performance without the expense of a complete infrastructure overhaul.
Benefits of 2.5 Gbps Ethernet
The adoption of 2.5 Gbps Ethernet offers numerous advantages to businesses and individuals alike:
- Enhanced Data Transfer Speeds: With 2.5 times the bandwidth of 1 Gbps Ethernet, this new standard enables faster file transfers, reduced latency, and improved overall network performance.
- Energy Efficiency: 2.5 Gbps Ethernet delivers increased performance with reduced power consumption, making it an environmentally friendly and cost-effective solution.
- Scalability: This technology provides an ideal stepping stone for organizations looking to upgrade their networks in preparation for even faster Ethernet standards in the future.
- Backward Compatibility: 2.5 Gbps Ethernet devices are compatible with existing 1 Gbps and 10 Mbps Ethernet equipment, simplifying the upgrade process.
Real-World Applications of 2.5 Gbps Ethernet
The superior speed and efficiency of 2.5 Gbps Ethernet make it a sought-after technology for various applications,
including:
-
Data Centers: With the ever-increasing demand for higher data transfer rates and lower latency, data centers stand to benefit greatly from the adoption of 2.5 Gbps Ethernet technology. This enhanced performance facilitates seamless server-to-server communication and efficient data storage and retrieval.
-
Enterprise Networks: Businesses with large networks can experience improved productivity and collaboration by upgrading to 2.5 Gbps Ethernet. Faster file transfers, reduced lag times in video conferencing, and more efficient handling of bandwidth-intensive applications all contribute to a smoother and more effective work environment.
-
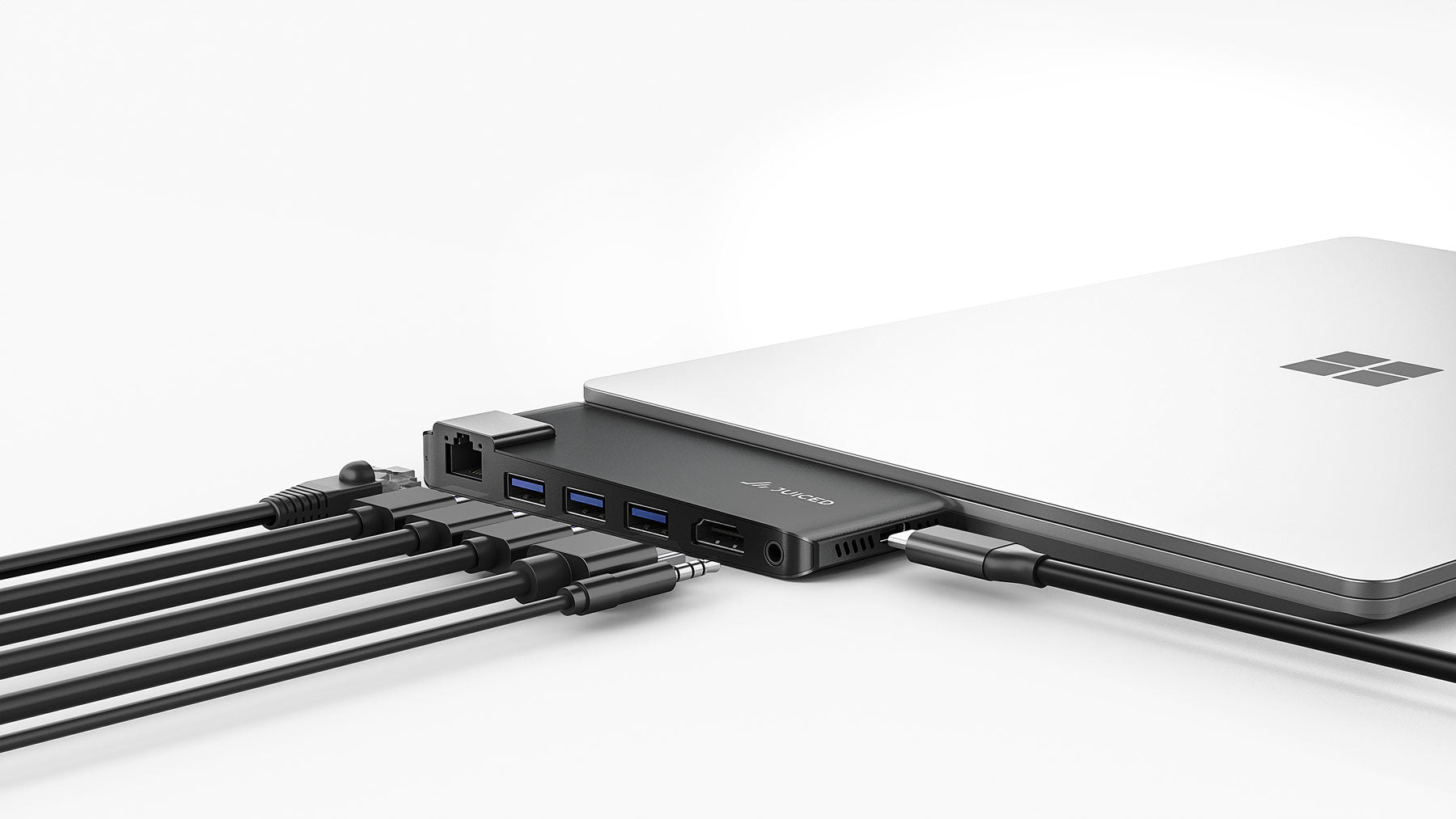
Gaming and Streaming: For avid gamers and content creators, 2.5 Gbps Ethernet provides a significant boost in performance, leading to a better online gaming experience and smoother streaming capabilities. This ensures minimal buffering and reduced latency, resulting in an enhanced entertainment experience. You can easily upgrade your ethernet capabilities with adapters such as the RapidHUB. USB4 enables the future of ethernet connectivity easily.
-
Smart Home Automation: As the Internet of Things (IoT) continues to expand, 2.5 Gbps Ethernet offers a robust solution for smart home devices. The increased bandwidth and speed allow for seamless integration and communication between various connected devices, paving the way for a truly connected and efficient smart home ecosystem.
Hardware Requirements and Compatibility
Upgrading to 2.5 Gbps Ethernet typically involves updating key network components, such as:
-
Network Interface Cards (NICs): To fully leverage the capabilities of 2.5 Gbps Ethernet, it is essential to equip your devices with compatible NICs. Many modern motherboards come equipped with 2.5 Gbps Ethernet ports, while others may require the addition of a standalone NIC.
-
Switches and Routers: Upgrading your network infrastructure to support 2.5 Gbps Ethernet may necessitate replacing or supplementing existing switches and routers. Look for devices that specifically support the 2.5 Gbps Ethernet standard for optimal performance.
-
Cabling: While 2.5 Gbps Ethernet is designed to work with existing Cat5e and Cat6 cables, upgrading to higher-quality Cat6a or Cat7 cables can further enhance performance and ensure the integrity of your data transmissions.
Ethernet Standard Data Transfer Speed Year Introduced 10BASE-T (10 Mbps) 10 Mbps Early 1990s 100BASE-TX (Fast Ethernet) 100 Mbps Mid-1990s 1000BASE-T (Gigabit Ethernet) 1 Gbps Late 1990s 10GBASE-T (10 Gigabit Ethernet) 10 Gbps Mid-2000s 2.5GBASE-T (2.5 Gbps Ethernet) 2.5 Gbps 2010s
The Future of Ethernet Technology
As the demand for faster and more reliable network connections continues to grow, Ethernet technology will undoubtedly continue to evolve. The development of standards such as 5 Gbps, 25 Gbps, and even 100 Gbps Ethernet is already underway, promising even greater advancements in the world of networking.
Organizations and individuals who invest in 2.5 Gbps Ethernet today will be well-positioned to adapt to these future innovations, ensuring that their networks remain cutting-edge and able to support the ever-increasing demands of our digital world.