DisplayLink vs Thunderbolt 4: Understanding the Key Differences
Introduction
In the ever-evolving world of technology, staying up-to-date with the latest advancements is crucial. Among these advancements, DisplayLink and Thunderbolt 4 have gained significant popularity in recent years. In this article, we will dive deep into the differences between these two technologies, their use cases, and help you make an informed decision on which is the best choice for your needs.
What is DisplayLink?
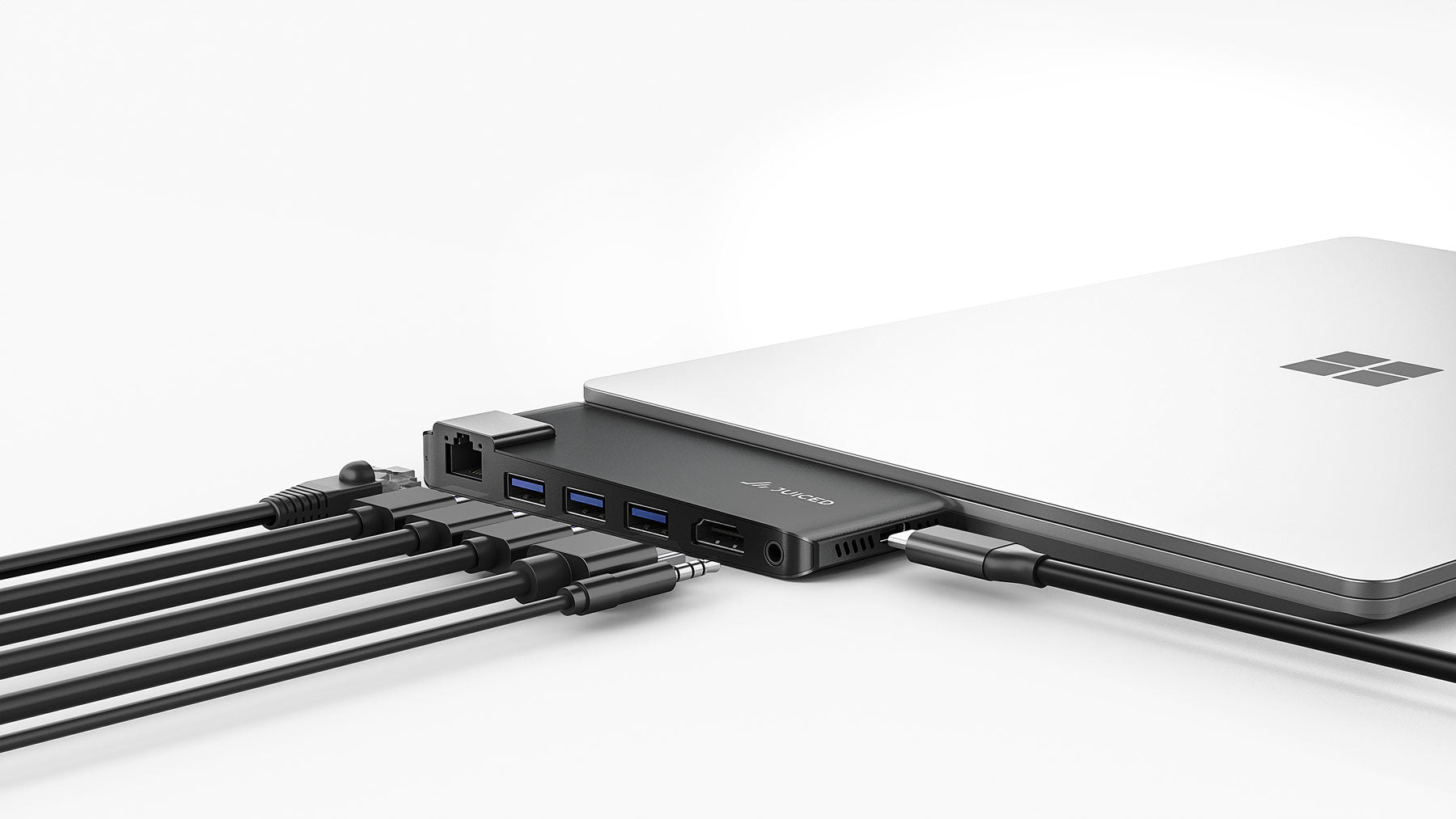
DisplayLink is a technology that allows you to connect multiple displays to your computer using a single USB connection. By leveraging the power of USB, DisplayLink simplifies the process of setting up and managing multiple monitors, making it an ideal solution for multi-monitor workstations, digital signage, and other applications that require multiple display outputs.
Key Features of DisplayLink:
- Connect multiple displays using a single USB connection
- Supports resolutions up to 4K
- Compatible with a wide range of devices, including PCs, laptops, and tablets
- Cost-effective solution for multi-monitor setups
What is Thunderbolt 4?
Thunderbolt 4 is the latest iteration of the high-speed, versatile connection standard developed by Intel. It combines the best features of USB, DisplayPort, and PCI Express, allowing you to transfer data, output video, and charge devices using a single cable. Thunderbolt 4 is an all-in-one solution that provides unparalleled performance and convenience.
Key Features of Thunderbolt 4:
- Transfer data at speeds up to 40Gbps
- Support for multiple 4K displays or a single 8K display
- Can provide up to 100W of power for charging devices
- Daisy-chaining capabilities for connecting multiple devices
Comparing DisplayLink and Thunderbolt 4
Now that we have a basic understanding of DisplayLink and Thunderbolt 4, let's compare their key features and differences to help you make an informed decision.
1. Display Capabilities
| Feature | DisplayLink | Thunderbolt 4 |
|---|---|---|
| Display Capabilities | Supports up to 4K resolution | Supports up to two 4K displays or one 8K display |
| Data Transfer Speeds | Depends on USB connection (5Gbps to 10Gbps) | Up to 40Gbps |
| Compatibility | Wide range of devices with standard USB port | Devices with a specific Thunderbolt 4 port |
| Power Delivery | No power delivery capabilities | Up to 100W of power for charging devices |
| Cost | Cost-effective solution | Higher price due to specialized hardware |
While both DisplayLink and Thunderbolt 4 can support multiple displays, Thunderbolt 4 offers superior performance in terms of display resolution and refresh rates. Thunderbolt 4 can support up to two 4K displays or a single 8K display, whereas DisplayLink is limited to supporting 4K displays.
2. Data Transfer Speeds
Thunderbolt 4 outperforms DisplayLink in terms of data transfer speeds. With the capability to transfer data at speeds up to 40Gbps, Thunderbolt 4 is significantly faster than DisplayLink, which relies on the USB connection's speed, typically ranging from 5Gbps to 10Gbps.
3. Compatibility
DisplayLink has an advantage in terms of compatibility, as it works with a wide range of devices, including PCs, laptops, and tablets, with a standard USB port. Thunderbolt 4, on the other hand, requires devices with a specific Thunderbolt 4 port, limiting its compatibility to newer devices.
4. Power Delivery
Thunderbolt 4 can provide up to 100W of power for charging devices, making it a convenient solution for powering laptops and other devices without the need for an additional power source. DisplayLink does not offer power delivery capabilities.
5. Cost
DisplayLink is generally a more cost-effective solution for multi-monitor setups, as it relies on standard USB connections and does not require expensive cables or adapters. Thunderbolt 4, while offering superior performance, comes with a higher price tag due to the specialized hardware required.
Conclusion
In summary, DisplayLink and Thunderbolt 4 each have their unique advantages and drawbacks. DisplayLink is a cost-effective solution for multi-monitor setups, while Thunderbolt 4 offers